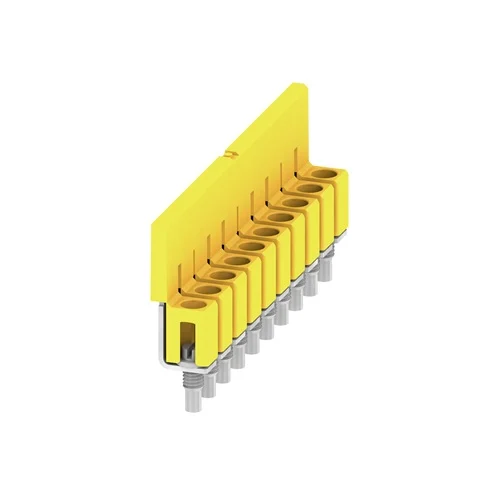
1. Control Cabinet Potential Distribution
Installed within DIN rail assemblies to bridge ten consecutive W-Series terminal blocks, effectively distributing a single 24V DC or 230V AC supply line across multiple branch circuits without auxiliary wiring.
Problem Solved
Eliminates the labor-intensive process of creating wire jumpers, reducing installation time and removing the risk of loose connections or short circuits in high-density panels.
Potential distributionTerminal bridgingW-Series compatibilityDIN rail interconnect
2. Industrial Signal Grounding Arrays
Used in PLC marshalling racks to create a common reference potential (0V/Ground) for banks of sensor inputs or actuator outputs, ensuring signal integrity across the automation system.
Problem Solved
Provides a mechanically rigid, screw-fixed common bus that withstands industrial vibration, unlike push-in jumpers that may dislodge under stress.
Common potentialSignal integrityGround busVibration resistance
3. Process Automation Voltage Bridging
Deployed in power distribution modules for process control loops to link adjacent terminals, allowing for the rapid configuration of voltage groups in limited space environments.
Problem Solved
Optimizes cabinet space by replacing bulky external distribution blocks with inline terminal bridging, maintaining finger-safe protection (IP20) for maintenance personnel.
Voltage bridgingSpace optimizationFinger-safe designProcess control